Generating Public Private Rsa Key Pair Linux
A lost SSH public-key or a web service generates an SSH key but does not provide the public-key part to you. What to do now? There is a solution for this situation.
- Create Rsa Public Private Key
- Generating Public Private Rsa Key Pair Linux Free
- Generate Public Private Key Pair Linux
When you have an SSH key you need the public key to setup SSH passwordless login with SSH-key. But if you have lost the public key part but still have the private key, there is a way to regenerate the key.
Generate Private key with OpenSSL and Public key ssh-keygen for SSH; Use PHP to generate a public/private key pair and export public key as a.der encoded string; Private Key Encrypt and Public key DecryptionIn Java C#; X.509: Private / Public Key; RSACryptoServiceProvider encrypt and decrypt using own public and private key; Get. You can generate an SSH key pair directly in cPanel, or you can generate the keys yourself and just upload the public one in cPanel to use with your hosting account. When generating SSH keys yourself under Linux, you can use the ssh-keygen command. In the Number of bits in a generated key box, enter 2048. Click Generate to generate a public/private key pair. As the key is being generated, move the mouse around the blank area as directed. (Optional) Enter a passphrase for the private key in the Key passphrase box and reenter it in the Confirm passphrase box.
With the public key missing, the following command will show you that there is no public key for this SSH key.
The -l option instructs to show the fingerprint in the public key while the -f option specifies the file of the key to list the fingerprint for.
To generate the missing public key again from the private key, the following command will generate the public key of the private key provided with the -f option.
The -y option will read a private SSH key file and prints an SSH public key to stdout. The public key part is redirected to the file with the same name as the private key but with the .pub file extension. If the key has a password set, the password will be required to generate the public key.
To check the details of the generated public key execute the following command as shown above.
A message indicates that your public-private RSA key pair is being generated. At the prompt, press Enter to use the default location or enter a file in which to save the key and press Enter. If you want the additional security of a password for the key pair, enter a passphraseand press Enter. Select public key for the cloud server from the SSH Keys list and click Add Public Key. Enter the key name, select the region, and paste the entire public key into the Public Key field. Then click Add Public Key.
The output of this command shows the key size as the first column, the fingerprint as the second column and after the file name, the type is shown in brackets. In the example above, a 4096 bit RSA key.
Read more of my posts on my blog at http://blog.tinned-software.net/.
Related posts:
Introduction
Secure Shell (SSH) is an encrypted protocol used by Linux users to connect to their remote servers.
Generally, there are two ways for clients to access their servers – using password based authentication or public key based authentication.
Using SSH keys for authentication is highly recommended, as a safer alternative to passwords.
This tutorial will guide you through the steps on how to generate and set up SSH keys on CentOS 7. We also cover connecting to a remote server using the keys and disabling password authentication.
1. Check for Existing Keys
Prior to any installation, it is wise to check whether there are any existing keys on the client machines.
Open the terminal and list all public keys stored with the following command:
The output informs you about any generated keys currently on the system. If there aren’t any, the message tells you it cannot access /.ssh/id_*.pub , as there is no such file or directory.
2. Verify SSH is Installed
To check if thw package is installed, run the command:
If you already have SSH, the output tells you which version it is running. Currently, the latest version is OpenSSH 8.0/8.0p1.
Note: Refer to our guide If you need to install and enable SSH on your CentOS system.
Steps to Creating SSH keys on CentOS
Step 1: Create SSH Key Pair
1. Start by logging into the source machine (local server) and creating a 2048-bit RSA key pair using the command:
If you want to tighten up security measures, you can create a 4096-bit key by adding the -b 4096 flag:
2. After entering the command, you should see the following prompt:
3. To save the file in the suggested directory, press Enter. Alternatively, you can specify another location.
Note: If you already have a key pair in the proposed location, it is advisable to pick another directory. Otherwise it will overwrite existing SSH keys.
4. Next, the prompt will continue with:
Although creating a passphrase isn’t mandatory, it is highly advisable.
5. Finally, the output will end by specifying the following information:
Now you need to add the public key to the remote CentOS server.
You can copy the public SSH key on the remote server using several different methods:
- using the ssh-copy-id script
- using Secure Copy (scp)
- manually copying the key
The fastest and easiest method is by utilizing ssh-copy-id. If the option is available, we recommend using it. Otherwise, try any of the other two noted.
1. Start by typing the following command, specifying the SSH user account, and the IP address of the remote host:
If it is the first time your local computer is accessing this specific remote server you will receive the following output:
2. Confirm the connection – type yes and hit Enter.
3. Once it locates the id_rsa.pub key created on the local machine, it will ask you to provide the password for the remote account. Type in the password and hit Enter.
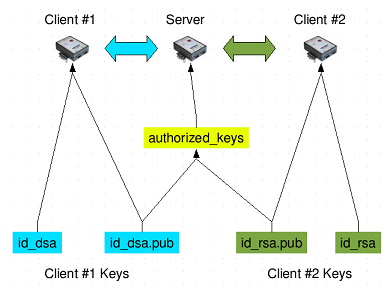
4. Once the connection has been established, it adds the public key on the remote server. This is done by copying the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file to the remote server’s ~/.ssh directory. You can locate it under the name authorized_keys.
5. Lastly, the output tells you the number of keys added, along with clear instructions on what to do next:
1. First, set up an SSH connection with the remote user:
2. Next, create the ~/.ssh directory as well as the authorized_keys file:
3. Use the chmod command to change the file permission:
chmod 700 makes the file executable, while chmod 600 allows the user to read and write the file.
4. Now, open a new terminal session, on the local computer.
5. Copy the content from id_rsa.pub (the SSH public key) to the previously created authorized_keys file on the remote CentOS server by typing the command:
With this, the public key has been safely stored on the remote account.
1. To manually add the public SSH key to the remote machine, you first need to open the content from the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file:
2. As in the image below, the key starts with ssh-rsa and ends with the username of the local computer and hostname of the remote machine:
3. Copy the content of the file, as you will need later.
4. Then, in the terminal window, connect to the remote server on which you wish to copy the public key. Use the following command to establish the connection:
5. Create a ~/.ssh directory and authorized_keys file on the CentOS server with the following command:
6. Change their file permission by typing:
7. Next, open the authorized_keys file with an editor of your preference. For example, to open it with Nano, type:
Create Rsa Public Private Key
8. Add the public key, previously copied in step 2 of this section, in a new line in (under the existing content).
9. Save the changes and close the file.
10. Finally, log into the server to verify that everything is set up correctly.
Once you have completed the previous steps (creating an RSA Key Pair and copying the Public Key to the CentOS server), you will be able to connect to the remote host without typing the password for the remote account.
All you need to do is type in the following command:
If you didn’t specify a passphrase while creating the SSH key pair, you will automatically log in the remote server.
Otherwise, type in the passphrase you supplied in the initial steps and press Enter.
Once the shell confirms the key match, it will open a new session for direct communication with the server.
Although you managed to access the CentOS server without having to provide a password, it still has a password-based authentication system running on the machine. This makes it a potential target for brute force attacks.
You should disable password authentication entirely by following the outlined steps.
Note: Consider performing the following steps through a non-root account with sudo privileges, as an additional safety layer.
1. Using the SSH keys, log into the remote CentOS server which has administrative privileges:
2. Next, open the SSH daemon configuration file using a text editor of your choice:
3. Look for the following line in the file:
Generating Public Private Rsa Key Pair Linux Free
4. Edit the configuration by changing the yes value to no. Thus, the directive should be as following:
5. Save the file and exit the text editor.
6. To enable the changes, restart the sshdservice using the command:
7. Verify the SSH connection to the server is still functioning correctly. Open a new terminal window and type in the command:
Generate Public Private Key Pair Linux
In this article, you learned how to generate SSH key pairs and set up an SSH key-based authentication. We also covered copying keys to your remote CentOS server, and disabling SSH password authentication.
Next, You Should Read: